Robotic Automation: Revolutionizing the Modern World One Task at a Time
By Write Holders | April 25, 2025
Introduction: Robotic Automation Process
Not long ago, the idea of robots assisting in our everyday lives seemed futuristic. Today, it’s a reality — robots are assembling cars, delivering packages, performing surgeries, and automating data entry in offices. This shift is called robotic automation, and it’s changing how we work, live, and even think.But robotic automation is not one single technology. It’s a combination of physical machines and intelligent software — each with its own roles, strengths, and challenges. Let’s explore this revolution in depth.
What Is Robotic Automation and Why It Matters More Than Ever
Robotic Automation refers to the use of machines or software bots to perform tasks traditionally done by humans. These tasks are often:
Why does it matter? Because automation can do these tasks faster, cheaper, and more accurately than humans — especially in large enterprises or industrial setups.
There are two key types:
⦿ Physical Robots (Hardware-based) – Machines that operate in the physical world.
⦿ Software Robots (RPA) – Programs that operate in digital environments, like office software or web apps.
Let’s break down both.
Physical Automation – The Role of Industrial and Service Robots
1. Industrial Robots: The Workhorses of Modern Manufacturing
These robots are found in factories and warehouses. They are designed for strength, speed, and consistency. They are programmable, precise, and often used in high-speed environments like car production.
Types of industrial robots:
⦿ Articulated Robots – Like mechanical arms, these can rotate and move in multiple directions.
⦿ SCARA Robots – Great for fast, accurate assembly in electronics.
⦿ Delta Robots – Lightweight, used in packaging for quick pick-and-place.
⦿ Cobots (Collaborative Robots) – Designed to safely work alongside humans.
Real-World Use Cases:
⦿ Tesla uses robotic arms for car assembly.
⦿ Foxconn employs thousands of robots to assemble iPhones.
⦿ Pharmaceutical firms use sterile robotic arms for packaging drugs.
2. Service Robots: Helping Humans in Daily Tasks
Service robots assist in non-industrial settings. They can work in homes, hospitals, airports, or customer service roles.
Examples:
⦿ Medical robots – Like the da Vinci Surgical System that helps surgeons operate with extreme precision.
⦿ Cleaning robots – Like iRobot’s Roomba.
⦿ Delivery bots – Used in universities or large campuses for delivering food or medicine.
⦿ Customer service bots – Interactive kiosks or humanoid robots that answer queries.
Service robots are becoming smarter with sensors, voice recognition, and even emotional detection to make them more “human-like” in their assistance.
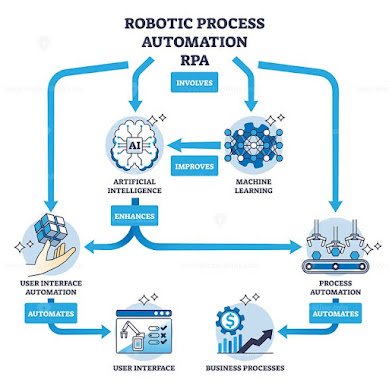
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) – Digital Labor for the Information Age
RPA is all about automating repetitive tasks done on a computer. Think of RPA as “virtual employees” that perform office tasks 24/7 — without rest or error.
Examples of tasks RPA can automate:
⦿ Reading and replying to customer emails
⦿ Extracting data from Excel files and filling forms
⦿ Copying information from invoices into accounting systems
⦿ Scheduling appointments
⦿ Generating regular reports
How It Works: RPA bots use the same interface a human would. They log in to apps, click buttons, enter data, and follow workflows.
Popular RPA Platforms:
⦿ UiPath
⦿ Automation Anywhere
⦿ Blue Prism
⦿ Microsoft Power Automate
These platforms often include AI and machine learning features, making bots even smarter.
Why Robotic Automation is a Game-Changer
1. Increased Efficiency
Robots don’t sleep or need breaks. They can operate non-stop, making them ideal for high-volume operations.
2. Cost Reduction
While the initial investment might be high, automation reduces the long-term cost of human labor, training, and human errors.
3. Higher Accuracy
Robots don’t make typos or forget steps. In fields like finance or healthcare, where accuracy is crucial, bots are a huge advantage.
4. Scalability
Need to process 10,000 invoices instead of 1,000? Just scale your RPA bots — no need to hire more staff.
5. Better Customer Experience
Automation speeds up response times, reduces wait periods, and even personalizes services using AI.
Real-World Applications of Robotic Automation
Banking and Finance:
⦿ Fraud detection using AI-powered bots
⦿ Real-time customer account validation
⦿ Automated compliance and audit reporting
Healthcare:
⦿ Automating insurance claims processing
⦿ Managing EHR (Electronic Health Records)
⦿ Robots assisting in minimally invasive surgeries
Retail and eCommerce:
⦿ Robots in warehouses for picking and packing
⦿ AI bots for customer support
⦿ Inventory tracking with real-time updates
Manufacturing:
⦿ Smart factories with robots and IoT sensors
⦿ AI-based quality inspection using computer vision
⦿ Predictive maintenance to avoid machine breakdowns
Government Services:
⦿ Automated form processing (passport, taxes)
⦿ AI chatbots for public queries
⦿ Document verification in legal systems
The Rise of Intelligent Automation – Beyond Just Bots
When RPA is combined with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), it becomes Intelligent Automation.
This allows bots to:
⦿ Understand context and language (NLP)
⦿ Learn from data and improve over time
⦿ Make decisions — not just follow scripts
Example: An intelligent bot reads thousands of customer complaints, understands which ones are urgent, and routes them to the right department with sentiment analysis.
Challenges Facing Robotic Automation
⦿ High Setup Costs: Especially for hardware robots and enterprise-grade RPA.
⦿ Job Displacement: Fear of robots taking over jobs is real. That’s why upskilling and human robot collaboration are key.
⦿ Integration Issues: Connecting bots with older systems can be technically complex.
⦿ Security Risks: Bots handle sensitive data and need strong cybersecurity protocols.
⦿Poor Process Selection: Not every task should be automated. If the process isn’t stable or well defined, automation may fail.
What’s Next – The Future of Robotic Automation
⦿ Hyperautomation: Going beyond RPA by combining AI, analytics, low-code tools, and process mining to automate everything possible.
⦿ Cloud Robotics: Robots connected through the cloud, sharing knowledge and updates globally.
⦿ Human-Robot Teams: Cobots and AI assistants will support humans in high-performance teams.
⦿ Autonomous Machines: From self-driving delivery bots to surgery-performing robots that learn from past operations.
⦿ Robots-as-a-Service (RaaS): Rent robots just like SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) — making automation affordable for small businesses too.
Conclusion: Augmentation, Not Replacement
The goal of robotic automation isn’t to take jobs away — it’s to amplify human capabilities. By automating boring or repetitive tasks, we free ourselves to focus on strategy, creativity, and empathy.
As this technology continues to evolve, the most successful companies and individuals will be those who embrace automation — not to replace people, but to empower them.
Tags: #RoboticAutomation #RPA #SmartFactories #AIandRobotics #FutureOfWork #AutomationRevolution #WriteHoldersthisblog #website







1 Comments
Good article and well explained
ReplyDelete